Product Design vs. UX Design: Everything You Should Know
As we do more of our most important work online, the need for well-designed software has never been greater, from the instant chat apps that are essential for remote team collaboration to the video chatting apps that people rely on every day.
Product and UX designers are people that are in charge of making the app user-friendly and convenient. Good UX returns $100 on average for every $1 invested, and great product design is what made Apple the trillion-dollar brand it is today. But what’s the difference between the two? As a part of our services at SumatoSoft, we provide UI&UX design services. In this article, we’ll take a look at product design vs UX design, covering the ways in which they overlap and the different functions they serve in software development.
What Is UX Design
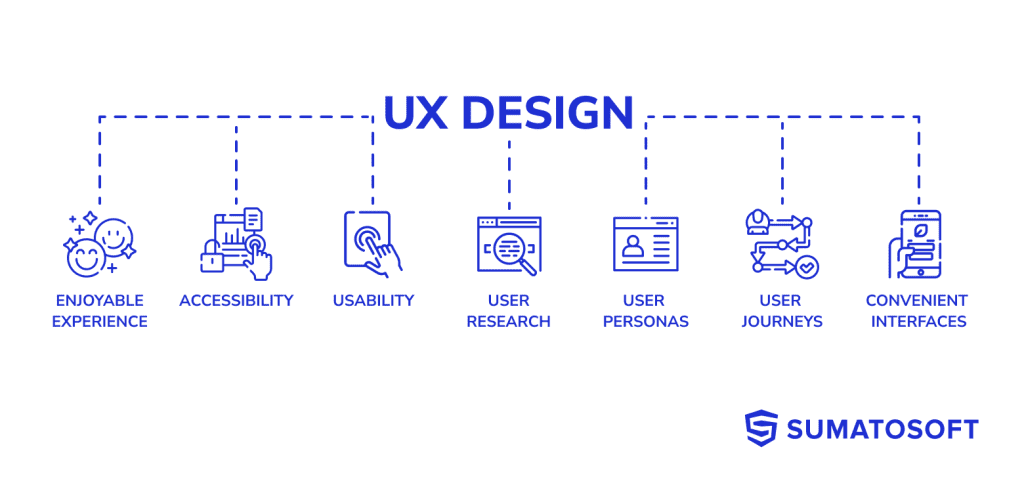
At its core, UX or User Experience Design, is an essential process that revolves around crafting an engaging, effective, and enjoyable experience for individuals interacting with digital platforms. The UX design methodology emphasizes accessibility, usability, and an innate understanding of the user’s desires and requirements, all while creating a product that is simple to understand and user-friendly.
This design discipline isn’t confined to the aesthetics of the product, but instead, it encompasses an end-to-end journey for users, from the first interaction to the last. It involves everything from user research, to developing personas, creating user journeys, wireframing, prototyping, and user testing. All these activities coalesce to shape a product or service that not only fulfills its intended purpose but also brings joy and ease to the user during its operation.
Looks aren’t everything; function is equally important, regardless of whether that’s in relation to SaaS website design, ecommerce website design, or anything in between.
Various organizations extend their expertise in the field of UX design services, and our team at SumatoSoft is a prime example of this. We pride ourselves on our skilled cohort of UI and UX designers who continually strive to advance and innovate in the landscape of User Experience Design. They approach each project with an unwavering commitment to optimizing functionality and enhancing the user’s interaction with the product. With our designers’ proficiency in UI and UX, we work in unison to ensure that our designs not only meet but exceed user expectations.
What Is Product Design
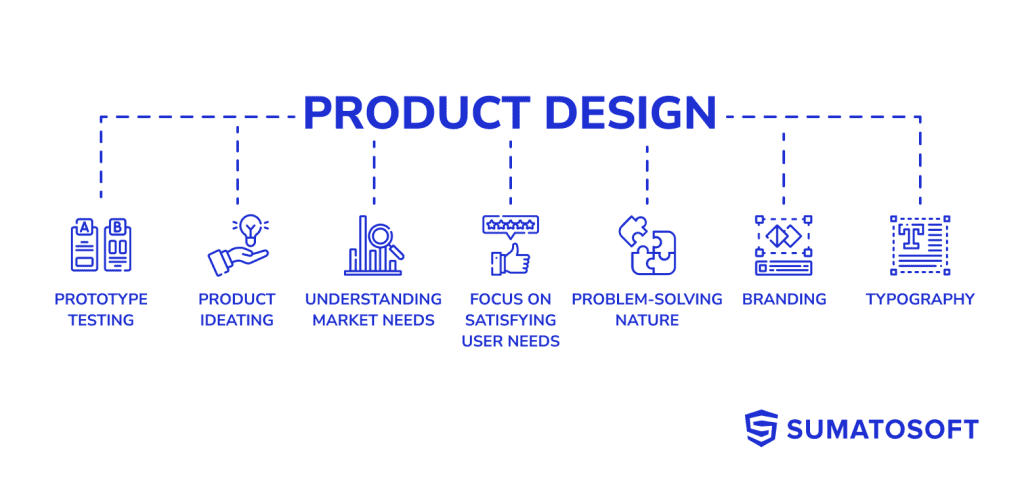
Product Design is a comprehensive, holistic process that incorporates the conception, design, development, and implementation of a product or service. It transcends the traditional notion of just ‘designing a product’, to incorporate all aspects from understanding market needs, ideating solutions, testing prototypes, to launching the final product.
Product design aims to create functional, valuable solutions that resolve real-world problems while satisfying the user’s needs and enhancing their overall experience. It involves a thorough understanding of user behaviors, market trends, and business objectives, leading to a product that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also serves its intended purpose effectively. Look at the 20 web design examples to see the way it looks.
The crux of product design lies in its problem-solving nature – it’s about identifying a gap in the market, understanding what the user requires, and then constructing a product that fills this gap in the most efficient and innovative way possible.
A product designer is much more of a generalist than a UX designer. Product designers are responsible for the overall look and feel of a website or app. This includes the user interface, branding and being the logo maker, typography, and visual design. They work closely with engineers to make sure the design is functional and will work in production.
In the 20th century, a product designer was an industrial designer, sketching new products, drawing up the plans for them, selecting materials, and testing the final product to make sure it could handle daily use.
A 21st-century product designer is doing the same thing in software—coming up with ideas, sketching wireframes, and then guiding the app’s design through its development into a real product. We wrote a separate article on best app design examples. We encourage you to look through it.
Product Design vs UX Design: Similarities
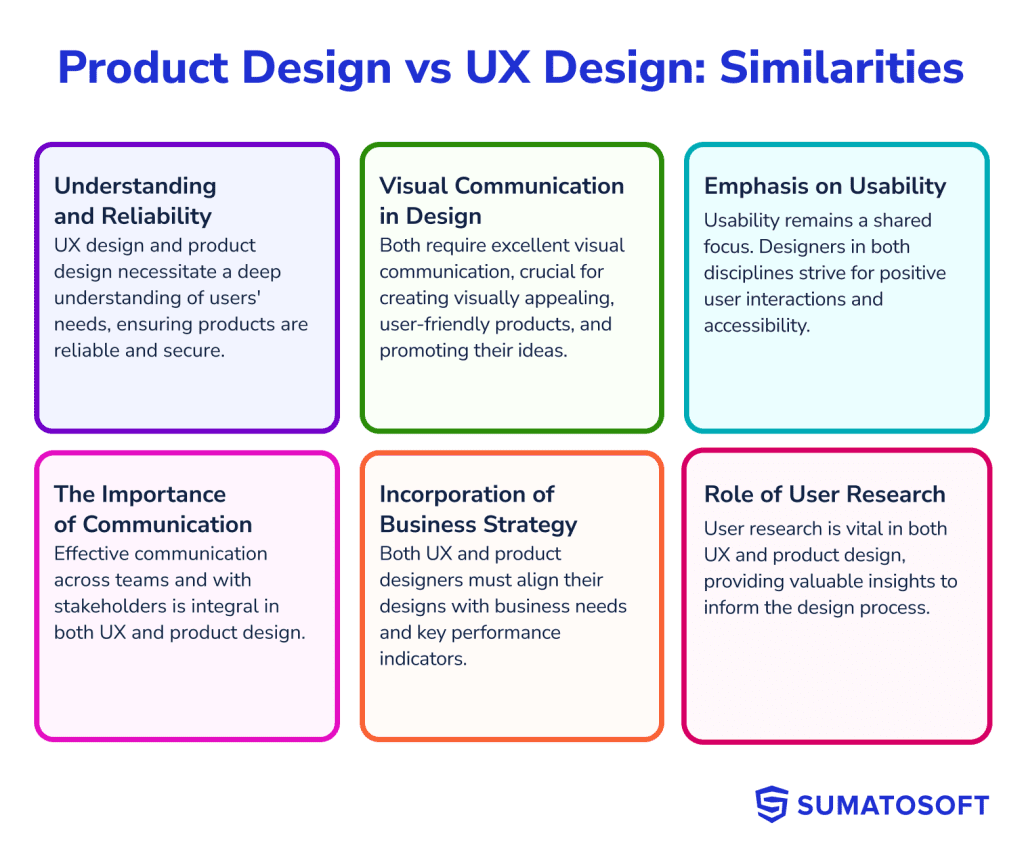
There are many similarities between UX design and product design. Both disciplines require an understanding of users and their needs. For example, health tech software must feel reliable and secure, and the best digital marketing tools need to make lots of information simple at a glance.
Visual Communication
Product design and UX design both require a good grasp of visual communication; this includes how different colors interact with each other, the principles of good typography, and how symbols and icons can communicate across language barriers.
That’s important for creating visually appealing products that are intuitive to use. Everything from the branding to the tiniest micro-interactions needs to serve the user experience. But visual communication is also important internally: in a big company, both types of designer will be creating mockups that “sell” their ideas to stakeholders outside the design and product teams. And in order to make the case for their ideas, they need to be able to take complex data around user journeys and visualize them in a way that’s legible and convincing.
Usability
Both disciplines share a focus on usability. In both cases, designers must think about how users will interact with their designs and how to make those interactions positive. They must also consider how to make their designs accessible for all users, regardless of ability or background.
Both types of design involve usability testing. In UX design this will involve endless A/B testing to increase successful journeys, whether that means a purchase or a complete onboarding. As the bar for “usability” gets higher every year, UX designers will be doing regular usability studies to keep the site up-to-date with user expectations.
Meanwhile, a product designer will be introducing their mockups and prototypes to different demographics to see how they interact with them. This could be a more holistic process than the UX designer’s data-driven testing, focused more on how the user feels and how easily they’re able to pick up and start using the product.
In both cases, the designers are unable to improve their work without incorporating user feedback. This is a big part of any designer’s job, whether they’re going through analytics or doing one-on-one interviews with customers. Interviews are more common in B2B settings, where keeping a few key accounts happy is crucial to having a profitable business and a product that serves its customers.
Effective Communication Is Integral to Both Disciplines
UX designers and product designers must be able to effectively communicate their ideas to stakeholders. They require buy-in from the developers who have to build the software and marketers who need it to fit with the brand. They have to be able to convince everyone that their solution is the correct one.
And both types of designer will need to communicate across teams to get their designs implemented. They’re not just convincing the managers that a design project is worth investing in, they need to work closely with hardware manufacturers or software engineers to get their designs implemented.
When the software team tells them that their mockup isn’t achievable, they need to be able to work with that team to find a compromise that works. In software, the technical details like loading times are as much a part of the user experience as anything the UX designers came up with, so the designers need to be fluent in the problems software developers deal with.
Both Need to Consider Business Strategy
Both UX designers and product designers have to take the business needs and strategy into account in their designs. Product designers are working on the future of the business, and the work of UX designers is pointless if it isn’t aligned with KPIs like net promoter score, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value.
If either designer wants to reimagine part of the product, there must be a solid business case for it with ways of evaluating success. They need to identify and work with customer personas, consider market research on those personas, and use business metrics to justify their ideas and measure their success. They also need to analyze competitors’ own versions of the problems they’re working on and think about how their business can uniquely position itself within the market.
Product designers are more likely to be in the long-term strategy meetings where they’re settling on a product roadmap for the next year. As those new features come online, it’s the UX designers who spend their days polishing up the features to best meet customer needs. In both cases they’re working towards the goal of product-market fit, which means they need to consider the business’s place in the market in everything they do.
Both Involve User Research
UX designers and product designers both require user research skills to do their jobs effectively. And that will involve using some of the same tools for collaborating on mock-up designs. They’ll both have to use video calls and shared whiteboards for user interviews, as well as tools like Google Analytics for measuring the performance of new changes.
User research happens throughout the design process. Often, product designers will be surveying key accounts and demographics to find out what needs the product isn’t meeting. Product designers are just as likely as UX designers to be consulting analytics to figure out what is and isn’t working. Both the “qualitative” and “quantitative” approaches are as likely to spark good ideas that the designers can prototype and bring to other stakeholders.
Product Design vs UX Design: Differences
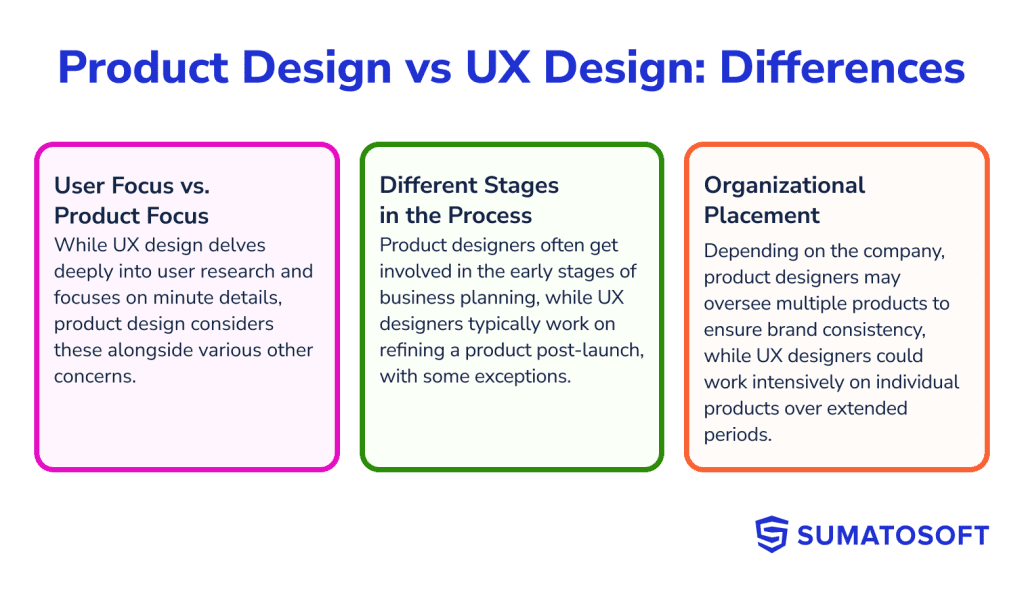
Despite their many similarities, Product and UX designers have some key differences.
UX Focuses on Users, not Product
The main difference between UX design and product design is that UX design focuses much more on the user and goes much deeper into the user research side of the design process; as far as product design is concerned, this is just one concern among many.
Also, UX designers are more likely to be involved in the tiny details of the product’s creation. For example, the placement of buttons and icons, and the exact implementation of the typographical style. In a web or mobile app, they’re more likely to focus on the frontend development either working with developers or writing some code themselves.
If a product is going to truly scale, it needs to be very accessible. Often, accommodations for people with mobility issues, visual impairments like color blindness, or cognitive disabilities can make a product easier to use for everyone. UX designers are going to be the ones responsible for accessibility concerns, as this is often very detailed work: making a button bigger, adding a drop-shadow or animation when a button is hovered over, or adding some helpful text to the page. This can involve tools like filters that simulate color blindness or calculate the “cognitive load” of taking in all the information on a page. This is technical work that’s best left to the UX designer, whereas product designers are focused on more high-level concerns.
An important part of any SaaS marketing strategy is clearly defining who the user is and what they want. Companies can’t get very far with that until they have product-market fit, and that’s where the product designer comes in. In hardware and software, product design focuses on the product, including what it looks like and how it’s made.
They’re Focused on Different Points in the Process
Product designers and UX designers play different but important roles in the product development process. Product designers are often there before the design process even begins, sat in the meetings where executives are discussing years-long business plans.
UX designers are often responsible for maintaining and improving a product long after it’s launched. (But of course, it varies from company to company. In some cases, UX designers might be doing user research long before an initial prototype is ready.)
But in UX, that means testing the user journey every time something new is added. Something as small as a new graphic on the ecommerce checkout page could distract users and reduce revenue for the business.
To help you understand how these roles differ, think of Jony Ive working on the initial designs for the iPhone and seeing it through to the final details and compare that to the teams of anonymous UX designers using the best app design practices to make existing apps incrementally better every year.
Different Placements within an Organization
How UX designers and product designers are “distributed” through a company will vary case by case. In big companies, product designers monitor several products at once as they get out of the initial stages and into real development. This ensures a consistency of style and functionality across the board, which is important for the brand.
In a big company, UX designers or teams will be somewhat siloed and working on individual products. Their user research work might be long and intensive, so they need to be seeing that through over several months to refresh a complex software product that has to serve millions of users.
How Product Designers and UX Designers Diverge

Anyone who’s worked in a small company knows that people have to wear several hats. Often, there’s just one designer around in the early days who has to launch the product and then keep reviewing it as it develops.
However, as the company grows into a bigger enterprise, it’s crucial that your UX and product designers have clearly defined roles and responsibilities, diverging along the lines we’ve discussed above.
These differences are important to consider when thinking about recruitment. The main difference between product and UX design is that a UX designer must place significant focus on the customer’s wants and needs to ensure the interface is user-friendly, whereas a product designer’s main focus is on the product and ensuring it’s cost-effective and meets the business’s needs.
Product and UX Designers at SumatoSoft
At SumatoSoft, we understand the critical interplay between UX and Product Design, and this understanding is reflected in our comprehensive custom software development services. With over a decade of experience serving Clients across 27 countries, our expertise lies in developing user-centric designs that align with business goals and target various devices and screen resolutions.
Our approach to UX and UI design services goes beyond crafting visually appealing interfaces. We delve into the intricacies of how end-users will interact with the product, guided by the wealth of expertise of our team. Our designers are proficient in usability, compatibility, and accessibility in web app development services. Our creative journey is helmed by an Art Director with 15 years of experience who excels at designing captivating UIs, logos, and brand style guides.
We are proud of our well-established design development processes, which allow us to:
- cut time on UI design development by 25%;
- keep the percentage of clients who come back to us with another project at 70%;
- reach the 98% mark of our client’s satisfaction rate, thanks to our firm commitment to deadlines and their needs.
Aligning with the core tenets of both UX and Product Design discussed in this article, we invite you to contact us to see how we can bring your vision to life while prioritizing user experience. We are happy to provide a free quote for your project.
Final Words From SumatoSoft
In conclusion, while the domains of UX and Product Design share a range of commonalities, they also hold significant distinctions. Both fields place high importance on understanding user needs, employing effective visual communication, enhancing usability, and utilizing effective communication techniques. However, their focal points differ: UX design emphasizes user-centricity and in-depth user research, while product design concentrates on the broader scope of the product, its look, and how it’s made.
Product designers play a critical role at the inception stage of a product’s life cycle, while UX designers focus on enhancing and fine-tuning the product post-launch, ensuring it continually meets user expectations. Additionally, the way these roles are distributed within an organization can greatly differ, depending on the size and structure of the company.
Both UX and Product Design are integral to creating successful products that not only meet user needs but also align with business strategies and market demands. They work in tandem to ensure a product’s success from conception to continual improvement, creating a comprehensive, user-friendly, and market-ready product that stands out in today’s competitive landscape.
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com