IoT Supply Chain: Real-life Use Cases & Challenges


Internet of Things (or just IoT for short) is a trending technology that is more and more broadly adopted by different industries: military, retail, construction, real estate, energy, etc.
Internet of Things has already changed a lot in our lives. For example, everybody uses a fitness bracelet or cars with GPS navigation applications daily. But IoT influences a lot more areas of human existence, including all stages of complex supply chain management. By leveraging IoT technology on different stages of the supply chain, companies get enormous advantages. However, IoT still has a huge potential which we expect to see in the future. To illustrate what that means, let’s refer to the history:
In the 1980s, the world saw the first commercially available mobile phone that weighed 790 g, offered 30 minutes of talk time, and had a price of 4000$. It wasn’t very popular, but this phone demonstrated the feasibility of such an idea as a portable communication device for everyone.
In 2007 at the convention in San Francisco, the public saw the first iPhone. The iPhone was powered by another awesome technology: a multi-touch screen, that became a sensation compared to widely used push-button phones. The iPhone revolutionized the phone market and changed the way we interact with phones.
Nowadays, almost everybody has one or more smartphones that have become a part of our daily lives. We truly believe that IoT is a technology that will revolutionize the way we interact with all devices! In the article, we explain the impact of IoT on the supply chain and familiarize you with real-life cases of leveraging IoT in inventory, logistics, manufacturing, IoT in Banking, and more.
Enjoy reading!
What is IoT (in short)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is very similar to the usual Internet that presents a network of connected computers. The difference is that IoT connects physical devices (so-called “things”) over the Internet. The devices range from gadgets in the ordinary household (kitchen appliances, thermostats, smart scale, light switches) to sophisticated things such as autonomous cars, industrial equipment, or smart cities. These things collect the data from the environment and transfer it to the cloud where the system accumulates the data and performs further filtering and analysis. The system can analyze different types of data, like geolocation, the temperature, the pressure, the state of something (like on/off), the air humidity, etc.
And here we come to the driving force of IoT popularity: the data.
The data is the cornerstone of any complex IoT system, while the volume of data within one IoT system is enormous. The number of connected devices exceeded 10 billion in 2019 and it is expected to reach the 30 billion mark by 2025! The volume of information the Internet of Things generates every year is even more impressive!

According to Statista, the data volume of Internet of Things connections worldwide reached 13.6 zettabytes in 2021. If you would like to know how big this number is, ask yourself what size the storage capacity of your computer is. Maybe, 2 – 4 terabytes – it would be great. One zettabyte contains 1 000 000 000 terabytes which is a hundred million times bigger than the memory of your computer!
But what to do with all that data? And how can the data be helpful in supply chain management?
It’s good to understand the term “supply chain” to answer these questions.
What is the supply chain?
The supply chain comprises all activities of different organizations required to convert raw materials to finished goods or services and deliver them to the final consumer.
A simplified model of supply chain management contains 6 stages:
- Raw material supplier.
Raw material suppliers gather natural resources or other raw materials and ship them to the next stage of the supply chain. Examples of raw materials are iron, beef, cotton, wool, barley, etc.
- Manufacturer.
Manufacturers are the next stage in the supply chain. They convert raw materials and natural resources into goods.
- Warehousing.
Warehouses are organizations that are legally allowed to store goods. Goods can include both raw materials and finished goods. So warehouses are useful across all the supply chain.
- Distributor.
Distributors deliver goods from manufacturers to the next stage of the supply chain.
- Retailer.
At that stage, retailers sell finished goods transferred by the distributors to the final customers.
- Final customer
Customers are people who buy final goods from retailers and use them for their purposes.
Supply chain management includes all these stages. Every stage may be supplemented and examined deeper, but that is not the topic of our discussion. The information in the model above is enough to describe the benefits that the Internet of Things brings to supply chain management.
How is IoT changing the supply chain?
Raw material supplier
This stage features one of the lowest levels of implementation of Internet of Things solutions. The future of IoT at that stage has a direct connection with the development of robots and the widespread use of robots in the gathering of natural resources. Nevertheless, some raw material suppliers have already benefited from the Internet of Things supply chain.
For example, on farms, IoT provides all kinds of data with the help of a network of connected sensors. IoT devices can gather information like soil moisture, chemical application, dam levels, and livestock health. The data allows farmers to maintain optimal conditions on their farms.
Manufacturer
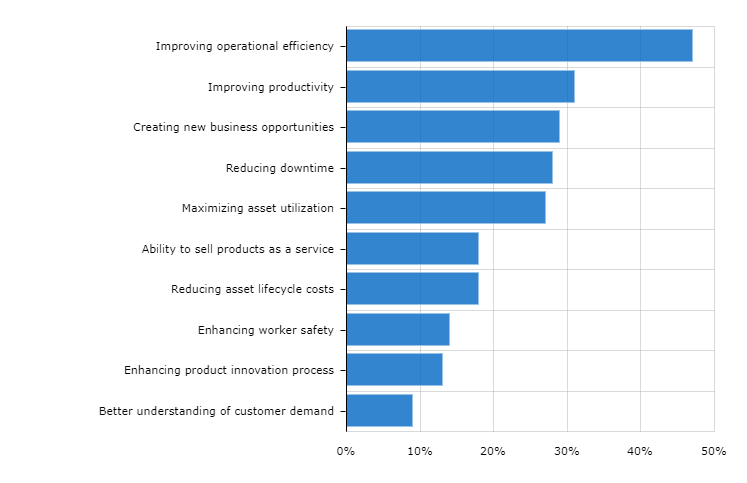
IoT supply chain allows manufacturers to reach maximum production efficiency as well as brings other benefits. The data that the IoT system generates can help to answer some big questions:
How to improve operational efficiency?
- How to reduce downtime in manufacturing
- How to increase asset utilization
- How to implement green strategies in your production process
According to the report from Morgan Stanley company, by implementing Internet of Things technology some manufacturers got answers to all questions above and managed to improve their operational efficiency.
IoT systems allow shifting away from logging the data manually or using traditional devices and provide more precision and timely data from sensors in manufacturing.
Continuous monitoring allows manufacturers to track hangtime in assembly and manufacturing operations in real-time. That helps to identify bottlenecks in the production process and make necessary adjustments. Furthermore, sensors can help to detect resource leaks, for example, by identifying broken machines with a very high level of energy consumption and either replacing or fixing them.
The Internet of Things also opens the way for proactive maintenance by tracking the machines’ health and notifying operators when maintenance is needed. Timely maintenance reduces downtime because workers can handle breakdowns or other maintenance issues before the machine actually breaks down. Predictive analytics allows forecasting system failures and machine breakdowns, hence saving a lot of money.
Unfortunately, the manufacturing process is accompanied by environmental pollution. That leads to climate change and deterioration of living conditions. With an IoT supply chain it’s possible to Integrate green strategies, like controlling the level of water use, creating less production waste, and implementing renewables. Using IoT in the supply chain, machine learning, and big data methods make it possible to track pollution from all sources all over the Earth – tracking pollution within one organization is a much easier task.
Distributors
Distributors are responsible for goods transportation. With IoT, they can offer real-time data on product locations and provide accurate time of goods delivery. By getting real-time information from carriers, airlines, border crossing stations, port authorities, meteorological satellites, and usual satellites, distributors can see the whole delivery route and optimize it taking into account real-time data from different sources.

Furthermore, the IoT system will immediately notify all interested parties if shipment delays or some changes in routing occurs. IoT supply chain gives full control throughout the route.
IoT sensors like Radio Frequency Identification tags get instant access to the content of any parcel and its storage conditions during transportation. That allows distributors to effortlessly track every single item, stay sure that none of the parcels will be lost, and bring more transparency to the whole delivery process.
IoT supply chain also brings benefits to a low temperature-controlled supply chain which is also called a cold chain. The cold chain relates to the transportation of perishable goods like food, fish, meat, flowers, or pharmaceutical products – all types of goods that are vulnerable to environmental conditions. With IoT sensors, any deviation from recommended conditions of storage is immediately detected, and an IoT system notifies distributors. IoT solves a big challenge for cold chains, saving money, goods, and public health.
Warehousing
By leveraging IoT sensors warehouses get an accurate and real-time inventory tracking system. By placing sensors on all goods, materials, or products, warehouses can easily track and analyze inventory positions, stock levels, and goods that enter and leave the warehouse in real-time. To build such a strong inventory system warehouses use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) sensors that track the location of all goods within the warehouse and control whether the product was moved.
Besides that, the combination of IoT technology and smart glasses increases picking performance in warehouses. IoT sensors provide a real-time map of goods, while smart glasses display the order picking instructions and information about the precise location of goods from the order. It results in better picking accuracy and the reduсtion in the amount of time needed to complete the order.
Environmental sensors help to monitor storage conditions and maintain the safety of perishable goods. They control the level of humidity, pressure, temperature, and other storage conditions, inform managers if some of them fall beyond the required level, and even can make an automatic condition adjustment.

Apart from that, some big storage can benefit from using Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) and almost fully automate the warehouse. Using proximity sensors and cameras, AMR can detect obstacles and avoid them by navigating around them. Moreover, robots analyze the environment and execute the movement only when success is assured. The system of AMR robots can transport goods within the warehouse without any human participation.
Retailer
IoT sensors speed up the process of loading and unloading goods because RFID tags keep all necessary information about the content of any parcel so that a retailer and any third party have accurate information about every parcel in the delivery.
IoT supply chain opens the way for new shopping technology without scanners, lines, and checkouts. Instead, you just take a good you want to buy, the IoT system identifies your choice and automatically adds the product to your chart. After you finish shopping and leave the shop, an IoT system withdraws the final cost of goods from your account. There is at least one example of such a type of store – you can explore it further in the article in the abstract about real-life use cases.
Why is IoT important in supply chain management?
The importance of the Internet of Things is hard to overestimate because it transforms supply chain management in several ways:
- Maximizes the effectiveness: By leveraging the Internet of Things in the supply chain manufacturers improve their operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and decrease resource leaks. Besides that manufacturers benefit from proactive maintenance of machines, hence reducing potential losses because of unexpected breakdowns.
- Helps to integrate green strategies: Using IoT in the supply chain, machine learning, and big data methods allows controlling the level of water use, production waste, and environmental pollution
- Provides real-time data on product locations: Distributors get the option to track products location in real-time and calculate the accurate time of goods delivery. All interested parties can be immediately alerted if the shipment delays or if some changes in routing occurs.
- Simplifies the cold chain management: With IoT sensors, any deviation from recommended conditions of storage for perishable goods is immediately detected, and an IoT system notifies distributors.
- Makes inventory tracking system more accurate: Thanks to IoT sensors warehouses can easily track and analyze inventory positions, stock levels, and goods that enter and leave the warehouse in real-time.
- Increases picking performance: The combination of IoT technology and smart glasses provides seamless workflow and performance that is impossible to achieve otherwise.
- Brings automation to warehouses: Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR), artificial intelligence, and IoT make it possible to build a fully automated system that will transport goods within the warehouse without any human participation.
- Speed up the process of loading and unloading goods: Thanks to RFID tags you get instant access to the content of any parcel.
- Opens the way to new shopping technology: You just take a good you want to buy, the IoT system identifies your choice and automatically adds the product to your chart, then withdraws the final cost of goods from your account after you finish shopping.
We consider the ways how the Internet of Things is changing the supply chain. Let’s get acquainted with real-life examples of how IoT has already changed some businesses and become a part of sophisticated and complex systems.
Real-life use cases of IoT in Supply chain
1. Aker
A great example of how a raw material supplier can benefit from IoT implementation is the Aker company. Aker enables proactive deep real-time crop observation to mitigate yield loss. Using drones, the network of 3d video sensors, big data methods, and machine learning, the IoT system allows farmers to identify crop damage from insects, disease, and other factors and make necessary decisions quickly.
2. DHL Logistics
DHL and its partner developed a bespoke, low-profile sensor to track roller cages throughout and between DHL facilities. Sensors feature minimum power consumption and a battery that has enough charge for 15 years. The data from sensors is used by operators via a cloud-based management portal to reduce shrinkage.
Using another IoT initiative, DHL benefits from 40% energy cost savings. Leveraging smart heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning the system makes real-time set-point adjustments based on anticipated weather conditions, building occupancy, and business activity, and maintains facility temperatures within a preferred operating range.
3. Amazon warehousing
Amazon is the world’s largest online retailer. Since 2012 Amazon has used robots in warehouses that carry shelves with products from worker to worker, scan barcodes and move packages. Nowadays, more than 200 000 robots are working inside Amazon’s warehouse. These robots work with hundreds of thousands of people and send goods all over the globe. You can see how utterly amazing it looks on youtube!
4. Volvo tracking
Volvo is a Swedish automotive manufacturer that has put IoT sensors in more than 350 thousand trucks. These sensors monitor conditions and send data for troubleshooting and analysis. Using IoT and artificial intelligence, Volvo Trucks reduce diagnostic time by 70% and truck repair time by 25%. Though, the biggest benefit is improved uptime. With more effective and proactive maintenance Volvo maximizes vehicles’ time on the road and minimizes the costs of service disruptions.
5. Maersk logistics company
Maersk is the Danish shipping company responsible for 18% of container trade in the world. The company built the Remote Container Management (RCM) system that monitors the storage conditions in 300 000 refrigerated containers. Thanks to accurate temperature and humidity control RCM provides optimal shipping conditions and reduces the chances for goods to become spoiled. Furthermore, full visibility into container conditions allows Maersk to reduce the cost and time spent on container inspection upon arrival because inspection organizations gain access to the data that containers have been kept in good conditions.
6. Amazon go store
Amazon Go store is a store of the next generation that became possible thanks to IoT technology. The store doesn’t have lines and checkouts, customers enter the store by using a special app on their smartphones, then take the products they want and leave.
The network of sensors and cameras tracks all your actions and goods you take, automatically adds products you took to your chart, calculates the final cost of goods, and then withdraws money from the bank account that is linked to the app on your phone.

The benefits are evident – less waiting time in lines, a fewer number of workers, fewer cases of stealing, and more satisfied and happy customers. You can see how amazing it looks on YouTube.
The Internet of Things brings new challenges to supply chain
All that sounds impressive and promising. However, the IoT supply chain still hides a lot of challenges, like:
1. Poor security of IoT devices
The number of IoT-based DDoS attacks is growing. The reason is the poor security of devices connected to the IoT system, which leads to misuse of the Internet of Things technology.

2. Low privacy level
IoT devices may collect and transfer sensitive information about their owners. IoT systems must provide security of data transfer and prevents unauthorized connections outside the system
3. Energy consumption
IoT devices are electronic devices that are expected to work continually for a long time. It’s especially crucial in industrial IoT systems that count thousands of little IoT devices. The maintenance of such a large IoT system can be a very time and cost-consuming task if the battery life of all IoT devices is not huge. That is why low energy consumption, low energy communication within a system, and long battery life are major issues to solve.
4. Talent shortage
There is a severe shortage of specialists that can build IoT systems, maintain them, and analyze the data from IoT devices. The educational system didn’t have enough time to adjust to new technological trends, which leads to the lack of people who can work with IoT technology.
5. A large volume of information
Any IoT system generates a large volume of data that should be transferred, stored, and processed. The traditional methods for these processes are not very useful when it comes to the transfer and storage of millions of terabytes of data. To solve this challenge IoT systems have to use LPWA technology, NoSQL solutions, and highly scalable cloud services.
Do you plan to develop an IoT project?
We can help you!
If you want to explore more possibilities of the Internet of Things, implement IoT technology, or get a comprehensive consultation about how to build an IoT system, the SumatoSoft team can help you.
With 9 years of experience on the global market and dozens of developed IoT projects, we know a lot of hidden hazards in IoT software development and develop the software in the right way.
The range of our services covers the whole development process ranging from the discovery phase to the programming and testing stages.
Conclusion
For the past few years, IoT devices and the data they collect have become proven drivers of higher efficiency and better service quality for the logistics industry and the supply chain. A simplified supply chain model comprises activities of 5 types of organizations: raw material suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, distributors, and retailers. Almost all stages of the supply chain have already benefited from IoT leverage.
IoT supply chain brings numerous benefits, like maximizing the effectiveness of manufacturers, providing real-time location of the products, simplifying the cold chain management, automating the warehouses, and much more.
However, there are still a lot of challenges the IoT supply chain is supposed to solve. The major challenge is data security and privacy because a lot of IoT devices manufacturers disregard even the basic security requirements for IoT systems.
The Internet of Things is a very powerful technology, and we believe that the benefits IoT will bring to the supply chain make the world a better place to live!
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com